1. An introduction to Virtual Wide Area Networking

Virtualized architecture is now being clustered and distributed beyond enterprise boundaries. Hybrid Clouds architectures are being built from combined private-enterprise and public-managed platforms. Desktop computers are rapidly being replaced or supplemented by laptops smartphones and tablet devices and these devices are spending more and more of their time outside of the traditional enterprise boundaries.
With all this IT virtualization taking place, where is the virtualization of the wide area networks that is needed to connect them all together? This video introduces the virtual wide area network and suggests how it can be used to accelerate the adoption and management of virtualized architectures.
2. Cloud VWANs - Use Case
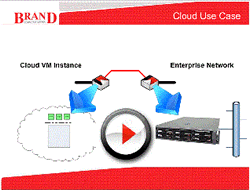
Connectivity between the managed cloud platform and the enterprise network will have a significant impact on the success of hybrid cloud computing. Brand Apollo, sitting at layer 2 can establish optimal connectivity between a VM in a managed cloud and the enterprise network by establishing a VLAN directly between the two.
The Apollo server software is installed on the edge of an enterprise network. The Apollo client software is installed onto a VM Image within a managed cloud architecture. When an instance containing an Apollo client is launched a VWAN tunnel is established from the VM through the virtual NIC back to the server. Apollo allows the remote VM to get an IP address directly from the DHCP server on the enterprise subnet. Once this is achieved all domain security, network neigbourhood and browsing are totally integrated and conformant with enterprise policies. The VM now behaves in every respect as if it were on the LAN with the Apollo server including using an IP address allocated to it by the server.
3. Mobile VWANs - Use Case
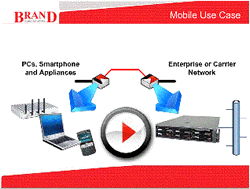
When the client and server are connected via a virtual wide area network the mobile device receives an IP address from the client node that is assigned to it by the server node.
From that moment onwards the mobile device behaves in every respect as if it were on a subnet of the remote enterprise or carrier network. Bandwidth, resilience and latency between the mobile device and the remote network can be enhanced by bonding two or more wide area networks together such as 3G networks, 4G network, Wi-Fi and satellite connections.
Connectivity is maintained seamlessly as the mobile device changes bearer such as when moving between 3G and Wi-Fi, or between 3G and 4G network.This feature addresses problems currently being experienced by carriers seeking to offload traffic from congested networks and by enterprises seeking to control the cost of their employees' mobility by using least cost networks.
4. Network of Networks using VWANs - Use Case
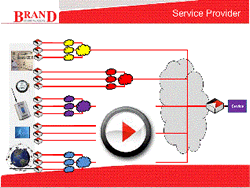
Wireless data usage is growing rapidly. In December 2009 Ericsson announce an historic cross over point where data exceeded voice for the first time. Their recent measurement of wireless networks traffic shows that global mobile data has nearly tripled in the last year, growing more than 10 times faster than voice.
Virtual Wide Area Networks allow carriers to manage multiple wide area networks, whether wired or wireless to act as if they were a single network. We call this Use Case the “Network of Networks”.


